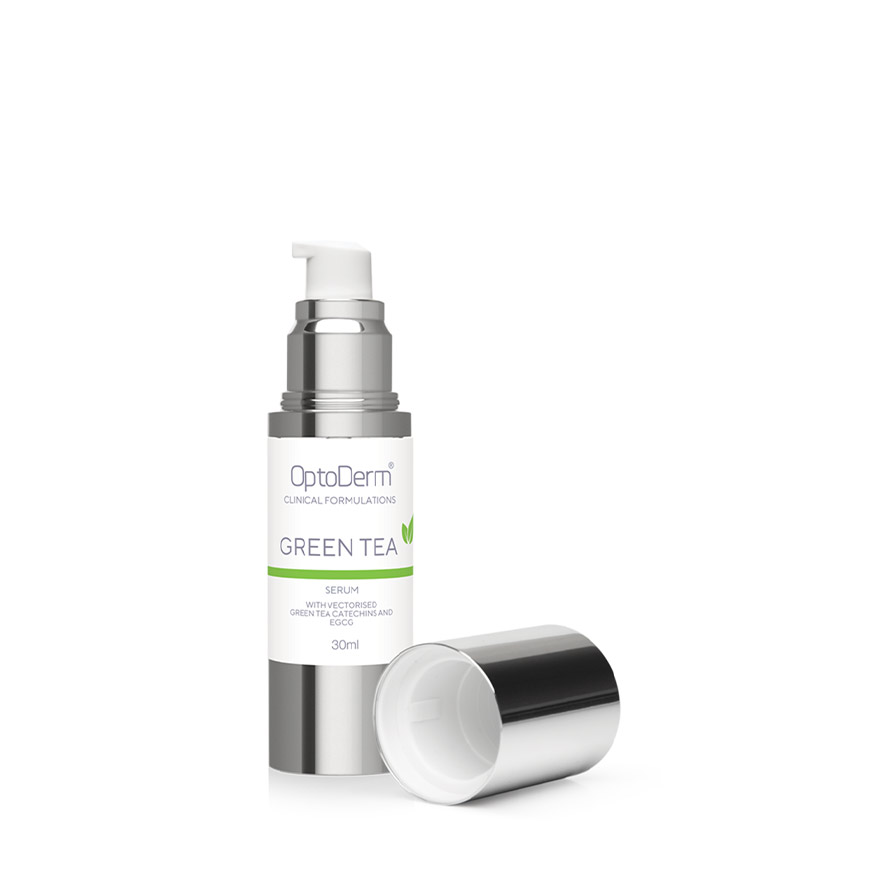
Features & Benefits
Powered by PenetrX, with proprietary vectorised green tea catechins and EGCG in a skin-similar phospholipid base.
Green Tea catechins play a role in multiple skin indications. Apart from being a powerful antioxidant (approximately 50 times stronger than vitamin C or reseveratrol), they facilitate a number of DNA protection and repair functions.
Key benefits:
Age Defying
The high concentration of catechins in Green Tea Mask deliver antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties to the skin that can help to slow the aging process, maintain the vitality of the skin, and improve its natural tone and glow. Catechins not only decrease skin cell damage directly, by diminishing levels of free radicals, but also inhibit the release of several proteolytic enzymes, especially matrix metalloproteinase enzymes (MMP), that destroy the collagen and elastin in our skin.
Acne Management
• EGCG displays apoptotic, sebosuppressive and anti-inflammatory effects on human sebocytes
• EGCG displays antibacterial effects on the P. acnes bacteria
• EGCG modulates AMPK–SREBP-1 and NF-kB/activator protein 1 (AP-1) signalling pathways, mediating the sebosuppressive and anti-inflammatory effects of EGCG respectively
• EGCG induces cytotoxicity of SEB-1 sebocytes via apoptosis
EGCG improves acne and is well tolerated in a clinical trial setting.
Sun Protection
Research has shown that green tea can reduce sun damage. This sun damage reduction is due to its ability to combat free radical damage, not by blocking ultraviolet radiation. It is not a replacement for sunscreen.
DNA Repair
it has the ability to repair DNA, protect against free radial damage, and boost the immune system.
Skin Disorders
Offering potent anti-inflammatory qualities, green tea can help to calm skin disorders such as rosacea and psoriasis.
Anti-Senescent Activity
Cellular senescence means a state of irreversible growth arrest by which normal cells lose the ability to divide generally after about 50 cell divisions. Some cells become senescent after fewer replication cycles as a result of DNA double-strand breaks.












Reviews
There are no reviews yet.